Quicksort algorithm with Go
Quicksort algorithm with Go
Quicksort algorithm is a “divide and conquer” algorithm. It takes the “pivot” element from the array and partitioning the other element into sub-arrays.
We can select the pivot with many ways but here I am going to select the last element with my example.
In case you want to understand what “divide and conquer” mean here:
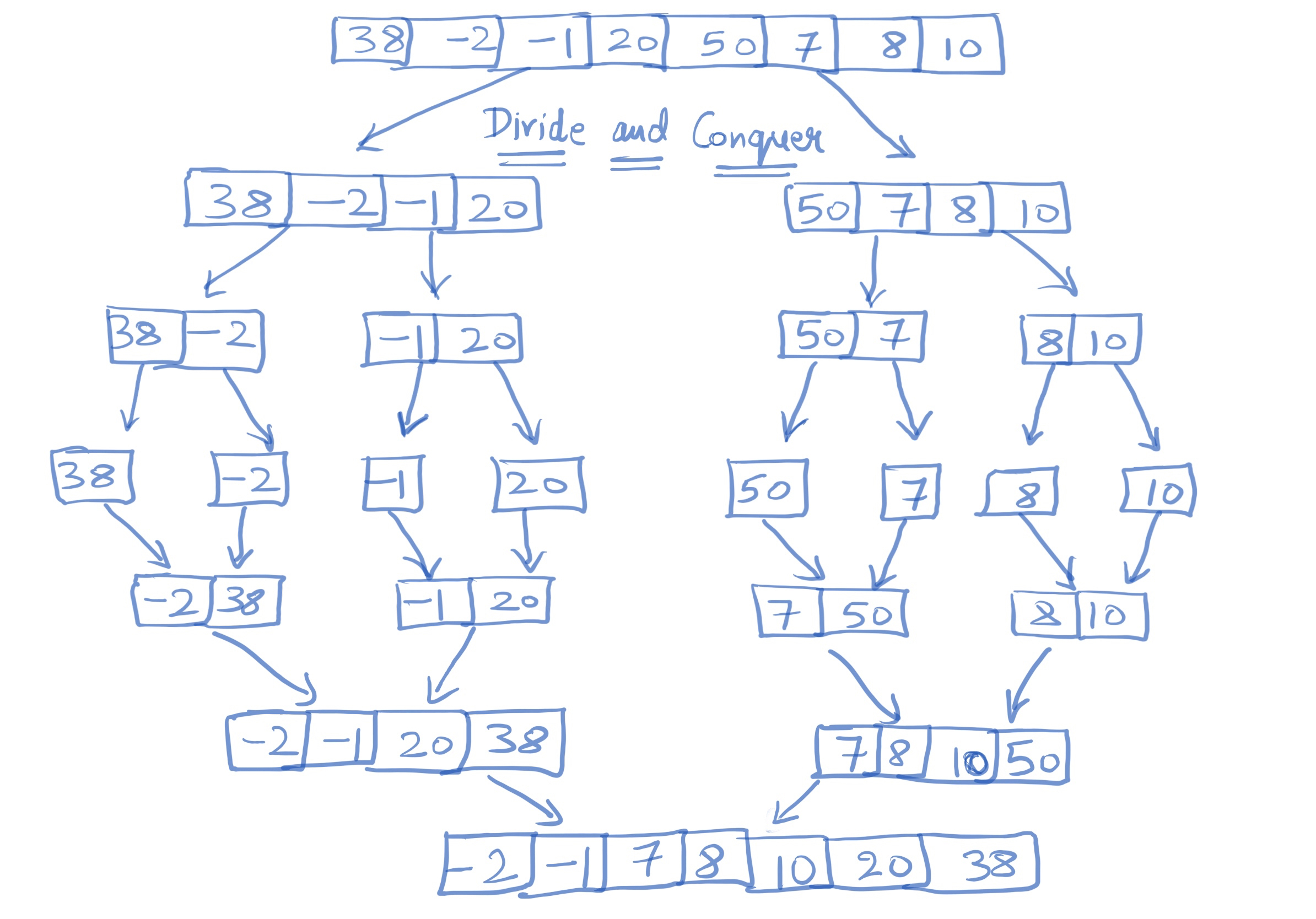
As you can see in screenshot above, it is partitioning the arrays we will be using the same approach here with go to create this algorithm.
Let’s assume we have the following arrays:
[38, -2, -1, 20, 50, 7, 8, 10]Here is our approach how we are going to create our pseudo code with the following way:
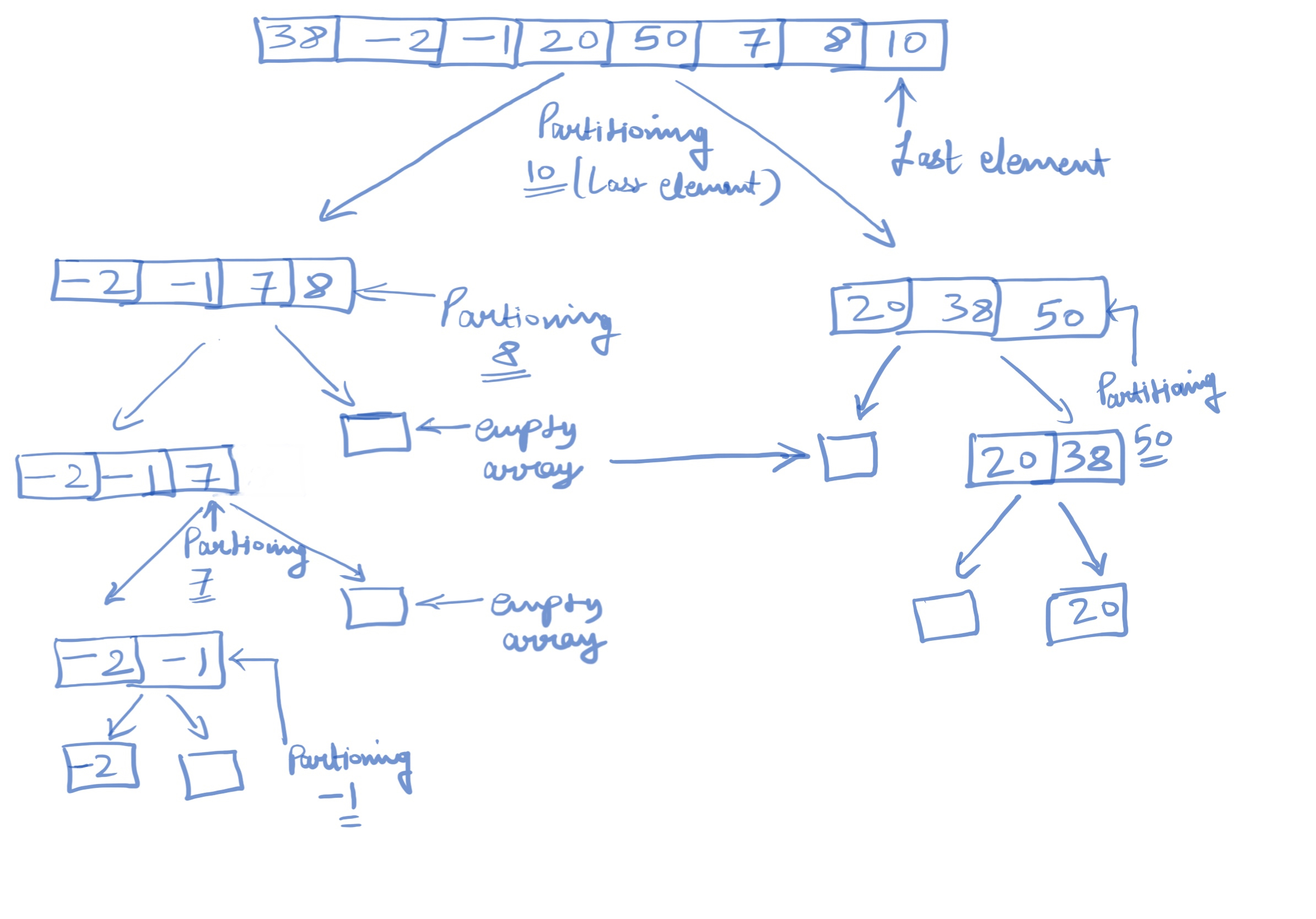
Pseudo code for our recursive algorithm:
quickSort(arr [], low, high) {
if low < high {
pi = partition(arr, low, high)
quickSort(arr, low, pi-1) // Before partition
quickSort(arr, pi+1, high) // After partition
}
}Let’s create a quick program using golang to show how we’re implementing this Pseudo code.
Firstly let’s create a simple logic with arrays:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var (
arr []int
low int
high int
)
arr = []int{38, -2, -1, 20, 50, 7, 8, 10}
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
fmt.Println(arr)
fmt.Println(low)
fmt.Println(high)
}
// Output
// [38 -2 -1 20 50 7 8 10]
// 0
// 7
As you can see, we just created a simple logic to make sure we are good at printing, now let’s implement quick sort function with our main program:
package main
func main() {
var (
arr []int
low int
high int
)
arr = []int{38, -2, -1, 20, 50, 7, 8, 10}
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
quicksort(arr, low, high)
fmt.Println(arr)
}
Let’s have a quick look at quicksort function logic
func quicksort(arr []int, low int, high int) {
if low < high {
// Partitioning..
pi := partition(arr, low, high)
// Before partitioning..
quicksort(arr, low, pi-1)
// After partitioning..
quicksort(arr, pi+1, high)
}
}
Let’s create a logic for our partitioning function
// Here, it's our return function
func partition(arr []int, low int, high int) int {
// Pivot
pivot := arr[high]
// Index
index := low - 1
for i := low; i <= high-1; i++ {
if arr[i] < pivot {
index++
// Swapping
arr[i], arr[index] = arr[index], arr[i]
}
}
// Swapping
arr[index+1], arr[high] = arr[high], arr[index+1]
return index + 1
}Notice here two things which I made a mistake when I was implementing the logic:
- Inside
partitionfunction, our loop starts withlowsince our quicksort function is recursive. So we don’t wanna mess up with arrays index here. - Swapping, since go returns multiple return value so swapping is much easier with go. We don’t need to define a separate function or
tempdeclaration.
Hopefully, we should get the following output:
[-2 -1 7 8 10 20 38 50]
In case, you want to see the complete program so here it is:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var (
arr []int
low int
high int
)
arr = []int{38, -2, -1, 20, 50, 7, 8, 10}
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
quicksort(arr, low, high)
fmt.Println(arr)
}
func quicksort(arr []int, low int, high int) {
if low < high {
// Partitioning..
pi := partition(arr, low, high)
// Before partitioning..
quicksort(arr, low, pi-1)
// After partitioning..
quicksort(arr, pi+1, high)
}
}
// Here, it's our return function
func partition(arr []int, low int, high int) int {
// Pivot
pivot := arr[high]
// Index
index := low - 1
for i := low; i <= high-1; i++ {
if arr[i] < pivot {
index++
// Swapping
arr[i], arr[index] = arr[index], arr[i]
}
}
// Swapping
arr[index+1], arr[high] = arr[high], arr[index+1]
return index + 1
}Time complexity
- Worst Time Complexity :
O(n^2) - Worst case can happen when array is already sorted
- Best time complexity :
O(nlogn) - Average Time Complexity :
O(nlogn)
Implemeting receiver function
Let’s try some way in go using receiver function, as we know that go has some receiver functional way. So, let’s modify our function and implment some receiver way.
We need to declare first the type here:
type quickSortAlgorithm []intAfter adding the type, we can declare our function something like with receiver function:
package main
import "fmt"
type quickSortAlgorithm []int
func main() {
var (
arr []int
low int
high int
)
arr = []int{38, -2, -1, 20, 50, 7, 8, 10}
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
// Notice here we need to declare the type creation here..
quicksortAlgo := quickSortAlgorithm{}
fmt.Println("Before quicksort")
quicksortAlgo.printArray(arr)
// Using this type, we can call our function like this..
quicksortAlgo.quicksort(arr, low, high)
fmt.Println("After quicksort")
quicksortAlgo.printArray(arr)
}
As you can see here, we have called our function using receiver quicksortAlgo.quicksort(arr, low, high). Also we are printing the array value from the receiver function quicksortAlgo.printArray(arr)
Alright, talk is enough. Let me show you the full code ;)
package main
import "fmt"
type quickSortAlgorithm []int
func main() {
var (
arr []int
low int
high int
)
arr = []int{38, -2, -1, 20, 50, 7, 8, 10}
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
quicksortAlgo := quickSortAlgorithm{}
fmt.Println("Before quicksort")
quicksortAlgo.printArray(arr)
quicksortAlgo.quicksort(arr, low, high)
fmt.Println("After quicksort")
quicksortAlgo.printArray(arr)
}
func (qa quickSortAlgorithm) quicksort(arr []int, low int, high int) {
if low < high {
// Partitioning..
pi := partition(arr, low, high)
// Before partitioning..
qa.quicksort(arr, low, pi-1)
// After partitioning..
qa.quicksort(arr, pi+1, high)
}
}
func (qa quickSortAlgorithm) printArray(arr []int) {
fmt.Println(arr)
}
// Here, it's our return function
func partition(arr []int, low int, high int) int {
// Pivot
pivot := arr[high]
// Index
index := low - 1
for i := low; i <= high-1; i++ {
if arr[i] < pivot {
index++
// Swapping
arr[i], arr[index] = arr[index], arr[i]
}
}
// Swapping
arr[index+1], arr[high] = arr[high], arr[index+1]
return index + 1
}
Your feedback is appreciated, please feel free to reach out to me on @rajendraarora16 for any suggestions.
Would be happy to say 👋